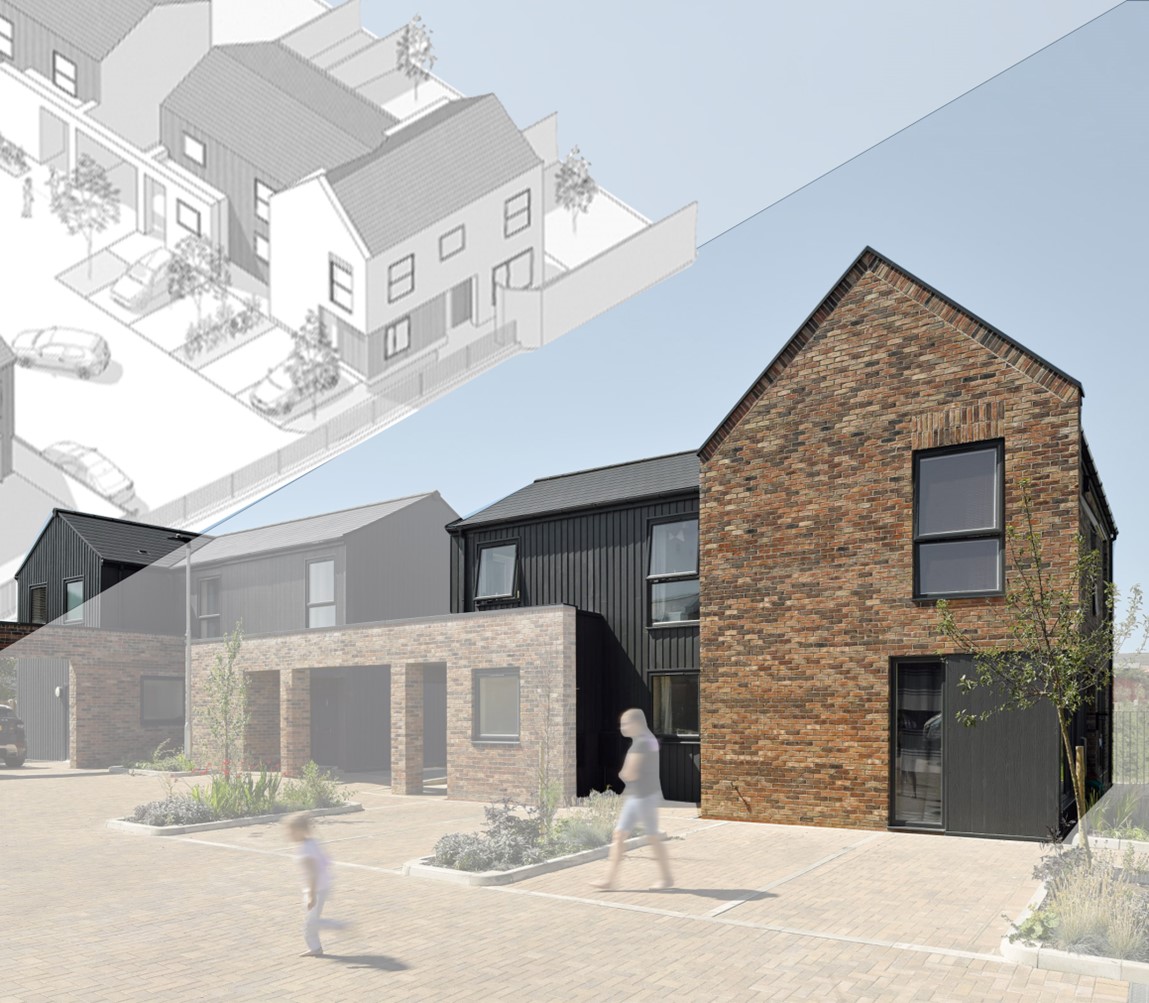
North Wingfield Road social housing complex.
Created on 25-11-2022
a) Design philosophy
According to the Housing Design Awards, the design of the North Wingfield project took a contemporary design approach, combining the features of local vernacular architecture - as adopted from local farms - with the developer's vision and requirements for flexible, sustainable and innovative housing (HDA, 2021). The architectural office DK -Architects explains that this fusion is represented by massing the morphology of the project, traditional architectural elements (e.g. Dreadnought brick (roof), Janinhoff brick (walls)) with modern elements such as large glazing and aluminium cladding. This combination of materials not only provides an aesthetically pleasing appearance, but also helps to capture heat, ultimately reducing heating energy consumption for at least seven months of the year (DK-A, 2021). In addition, several innovative features have been adapted, including the well-planned use of space and the clear conceptual plans that extends beyond the interior spaces to the shared courtyard, which serves as a social gathering place for the tenants.
The inspiration for the courtyard was derived from the local identity, the farmstead and the crew yard (HDA, 2021). At the same time, the use of a see-through fence, which extends the sightline into the rural surroundings, provides a calming splash of green colour in each residential unit. The semi-raised upper massing extends the courtyard and provides a semi-enclosed space that enhances the feeling of safety and security (DK-A, 2021). Meanwhile, the buildings in the front row clearly stand out from the surrounding buildings through the use of colours and materials and also serve as an entrance gate to the project (DK-A, 2021; HDA, 2021). Each dwelling has its own mini agricultural space, which has proven valuable for the well-being of the residents.
b) Construction process
The skeleton of the building utilises an off-site timber frame method of construction, adopting a semi-modular design principle (Davies & Jokiniemi, 2008). This construction method provides a structure with a superior thermal envelope that requires minimal maintenance and is a 'fit-and-forget' solution for the lifetime of the building. In addition, both labour and material costs were significantly reduced due to less reliance on craftsmanship and multiple suppliers. This is in line with the UK government plans to revamp construction regulations to encourage bold, creative and sustainable construction methods (Davies & Jokiniemi, 2008; Sterjova, 2017).
The construction process started with ground treatment, followed by the casting of the foundations on site. Meanwhile, the timber frames were manufactured off-site at the supplier's factory, which helped to reduce construction work and thus carbon emissions. The frames were then transported to the site for fixing and external treatment, and all the construction work ran in parallel (Wheatley, 2020). The overall process can be seen in Figure 1.
c) Sustainability integration
At the sustainability level, the project worked on several areas to maximise the adaptation of sustainability features and minimise the impact on the natural environment (HDA, 2021).
Creating sustainable buildings
Through sustainable design and layout (e.g. orientation, maximising daylight, optimising solar gain).
Creating high quality outdoor environments (e.g. public and private open spaces that provide shade and shelter and consider flood retention and multi-functional green spaces to protect wildlife).
Use of sustainable water management techniques (e.g. use of sustainable drainage systems and consideration of surface water run-off).
Use of sustainable waste management facilities for private and communal use (through the appropriate provision of waste and recycling bins).
Focus on reducing the use of non-renewable energy.
Reduction of carbon emissions
The project has been designed in accordance with the highest level of building regulations and sustainability standards, in line with the Government's 10-year timetable for all new homes to be carbon neutral by 2016.
Water recycling techniques (such as grey water and rainwater harvesting).
Sustainable Transport (reducing reliance on the private car, incorporating practical and accessible sustainable transport patterns).
d) Energy performance
One of the tools to assess building energy efficiency in the UK is the Energy Performance Certificate (EPC), which is defined by the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities as:
A rating scheme that summarises the energy efficiency of buildings; it includes a certificate that gives a property an energy efficiency rating from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient) and is valid for 10 years (DLUHC, 2014).
The EPC is produced using the Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP), which is defined by the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy as follows:
The method used to assess and compare the energy and environmental performance of properties in the UK [...] it uses detailed information about the property's construction to calculate energy performance (DBEIS, 2013).
The North Wingfield project has successfully achieved a (B) rating - equivalent to 84 out of a maximum possible 100 points with a high potential for an (A) rating equivalent to 95 points (DLUHC, 2021). This score is the result of
The use of high-performance materials with very good thermal transmittance properties (walls: 0.20 W/m²K, roof: 0.11 W/m²K, floor: 0.09 W/m²K).
Well-designed ventilation system that achieves a good air tightness indicator (air permeability 4.9 m³/h.m²).
Low consumption of primary energy of 94 kWh/m2.
Another indicator is the Environmental Impact Score (EIS), which shows the impact of a building on the environment through the estimated carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions calculated at the time of the EPC assessment (DLUHC, 2014). The higher the score, the lower the building's impact on the environment: like EPC labels, the environmental impact score is graded from A to G (DBEIS, 2014). The project generates 1.4 tonnes of CO2 annually. This is less than a quarter of the 6 tonnes emitted by an average household. By improving the EIS rating to A, CO2 production will be reduced to 0.3 tonnes, which will distinguish the project as one of the most environmentally friendly projects (DLUHC, 2021). Figure 2 shows the EPC and EIS breakdowns of the properties.
M.Alsaeed (ESR5)
Read more
->
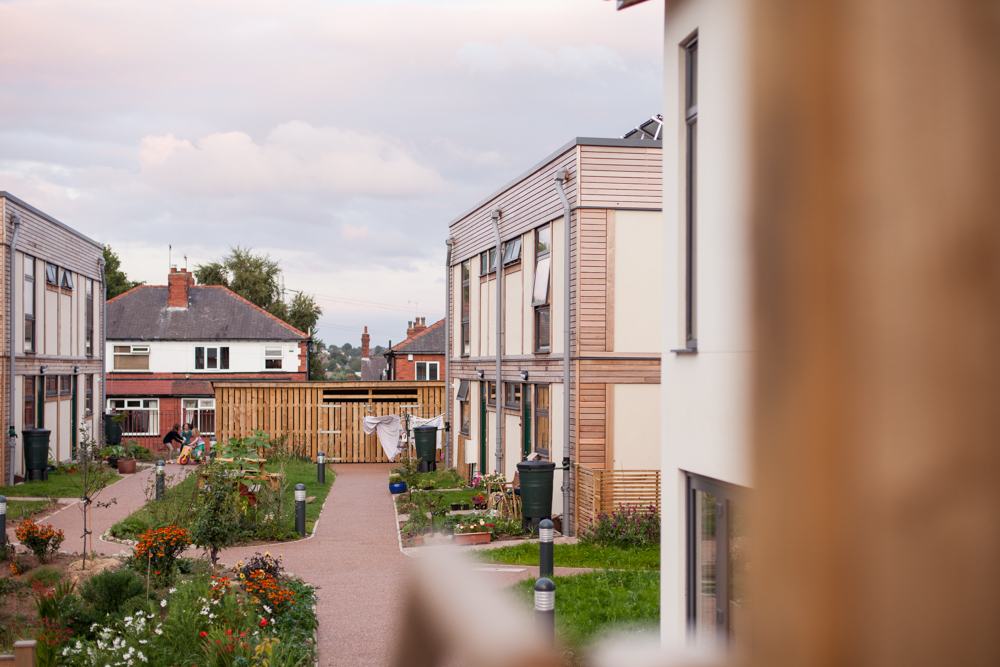

LILAC_Low Impact Living Affordable Community_Leeds
Created on 15-11-2024
Innovative aspects of the housing design/building
The model for LILAC is based on the Danish co-housing model: mixing private space with shared spaces to encourage social interaction. A plethora of green spaces include allotments, pond, a shared garden and a children’s play area. Akin to the private self-contained homes, the ‘common house’ includes a communal workshop, office, post room, food cooperative, kitchen, dining space, social space, bike storage, play area, guest rooms and laundry room. The LILAC community benefit from a large number of communal facilities including: a common house with shared laundry, kitchen, reading area and community area; car sharing; pooling household equipment and power tools; sharing common meals twice per week; growing food in the allotment; and looking for provisions in the local area (LILAC Coop, 2022b; ModCell, n.d.). A shared lifestyle whereby resources and amenities are combined, reduces energy use and saves money.
Construction and energy performance characteristics
Constructed under a Design and Build contract (Chatterton, 2015), LILAC boasts an innovative prefabricated ModCell construction that includes a low carbon timber frame insulated with straw-bale. Residents assisted with the labour, collectively adding the straw bale insulation. External walls and interior finishes are in a lime render, increasing benefits from passive solar heating through thermal mass. Air tightness was prioritised during construction, and triple-glazed windows help to decrease heat loss during winter, allowing for Mechanical Ventilation Heat Recovery Systems (MVHR) to regulate indoor air temperature. Further energy performance characteristics include solar thermal energy collection for space and hot water heating, 1.25kw solar PV array, with an extra 4kw on the common house (LILAC Coop, 2022b).
LILAC features a flood prevention system whereby a sustainable urban drainage system (SUDS) feeds the central pond. Roof rainwater runoff is collected into water butts that are later used to water the gardens. Overflow from water butts enters the central pond, which discharges into the public drainage system at a reduced rate. Furthermore, all ground surfaces of the site are permeable. Biodiversity planting and a permaculture design certificate course were integrated into the design at planning stage.
Major additional spending decisions were made whenever residents believed it would meet their core values and result in long term financial savings (Chatterton, 2015, p.68). Construction costs were therefore higher than the UK average – a 48 sqm one-bedroom flat cost £84,000 to build at a cost of £1,744 per sqm while the average costs in England were £1,200 per sqm. However, the annual heating demand of the homes is far less than the UK average of 140kWh/m² at around 30kWh/m², reducing energy consumption and bills up to two-thirds compared with existing UK housing stock (Chatterton, 2015, p.84).
Involvement of users and stakeholders
LILAC is owned by a cooperative, through the innovative equity-based model: Mutual Home Ownership Scheme (MHOS). The MHOS is a leaseholder approach (Chatterton, 2013) where residents purchase shares in the co-operative. The number of shares owned by each member is related in part to their income, and partly according to the size of their property. If someone earn a large income their house becomes more expensive, but another property subsequently becomes cheaper, thus conserving affordability. Affordable housing at LILAC is maintained as no more than 35% of net household income should be spent on housing (Chatterton, 2013; LILAC Coop, 2022a).
Minimum net income levels were set for each different house size to ensure a 35% equity share rate generates enough income to cover the mortgage repayments (Pickerill, 2015). The MHOS owns the homes and land and is made up of the residents who also manage LILAC. Members lease and occupy specific houses or flat from the MHOS. In effect, residents are their own landlords.
The building was financed by a combination of personal members invested capital, a long-term mortgage from the ethical bank Triodos, and a government grant of £420,000 from The Homes and Communities Agency’s Low Carbon Investment Fund, specifically to experiment with ModCell straw construction (Chatterton, 2013; Lawton & Atkinson, 2019). Each member makes monthly payments to the MHOS, who then pays the mortgage – deductions are made for service costs. In 2015, annual household minimum income for a home was set as at least £15,000.
‘Community agreements’ cover areas such as pets, food, communal cooking, use of the common house, management of green spaces, equal opportunities, vulnerable adults, the use of white goods, housing allocation and diversity, and garden upkeep (Chatterton, 2013; LILAC, 2021). “MHOS forms the democratic heart of the project” (Chatterton, 2013). All decisions are made democratically, using templates to generate and discuss proposals, explore pros and cons, generate amendments, and ratify decisions (Chatterton, 2013).
Relationship to urban environment
LILAC is in a highly integrated inner-city locality, situated in an urban neighbourhood of Leeds, on a site that was previously a school. Integrating with the wider community in West Leeds, the common house is used for “local meetings, film nights, meals and gatherings, workshops and has been used as the local polling station” (LILAC Coop, 2022b). LILAC has increased residents feeling of empowerment to participate in social action, working within the wider community to explore issues together and work for change. This has included supporting a local community association, local schools and holding charity and music events (LILAC, 2021).
Behaviour and wellbeing
LILACs community act in the knowledge that an adequate response to climate change and energy reduction takes shifting the way we live, enacting behavioural changes that contribute to a post-carbon transition. Decisions in cohousing are made as a community, rather than individual consumers or households. Residents report a much higher health satisfaction – from 58% to 76% – and life satisfaction – from 58% to 87% – compared to previous accommodation (LILAC, 2021). Both physical and mental health improvements have been reported since moving to the community due to LILAC’s “plentiful greenspace, sustainable travel options, better high air quality and natural light in the homes, greater social interaction and opportunities for socialising with neighbours” (LILAC, 2021). Further benefits of LILAC as a cohousing scheme include increased safety and wellbeing, natural surveillance and support for the elderly, reduced car numbers combined with car separation and car-free home zones to increase safety as well as reducing carbon emissions related to car use (Chatterton, 2013).
S.Furman (ESR2)
Read more
->
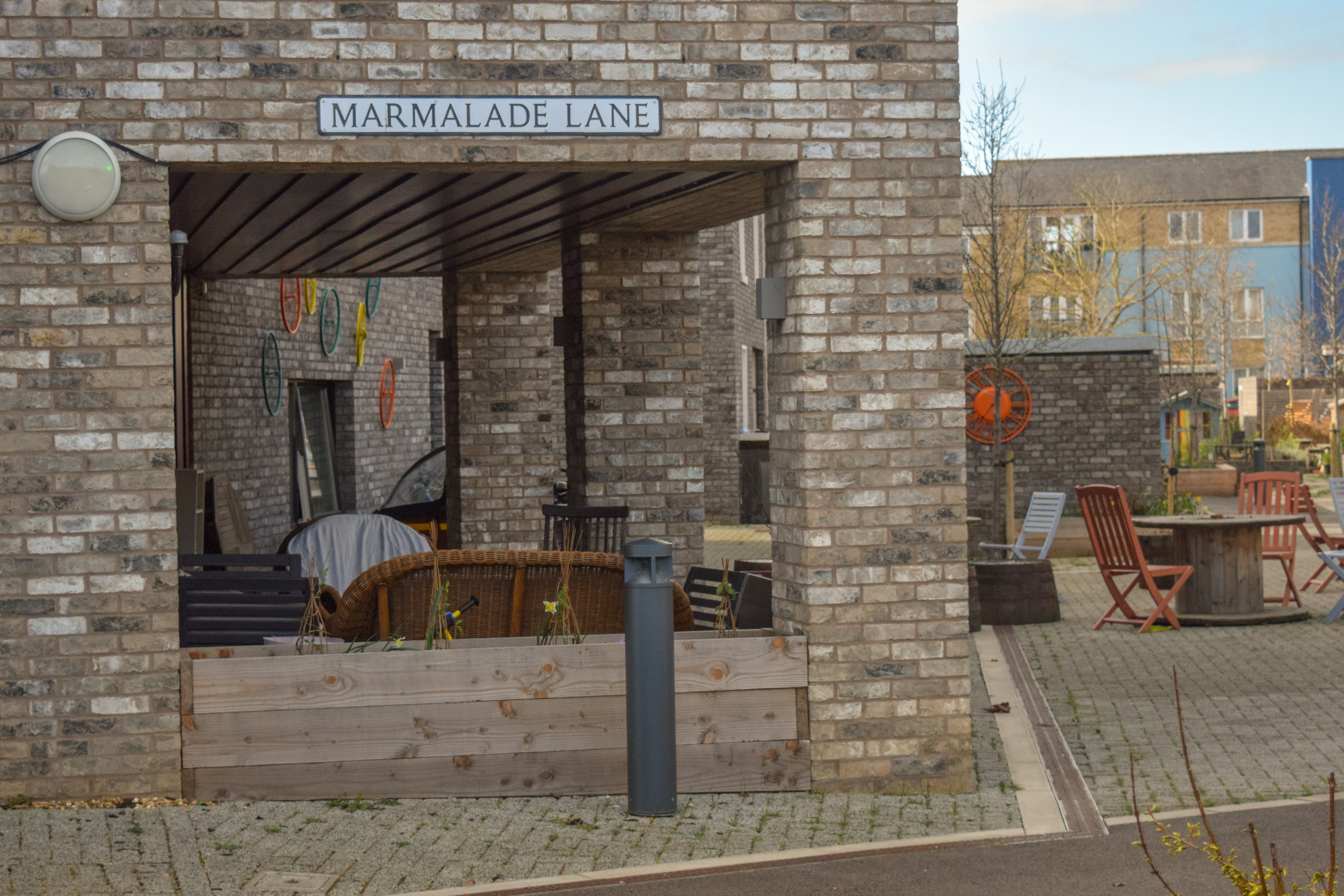

Marmalade Lane
Created on 08-06-2022
Background
An aspect that is worth highlighting of Marmalade Lane, the biggest cohousing community in the UK and the first of its kind in Cambridge, is the unusual series of events that led to its realisation. In 2005 the South Cambridgeshire District Council approved the plan for a major urban development in its Northwest urban fringe. The Orchard Park was planned in the area previously known as Arbury Park and envisaged a housing-led mix-use master plan of at least 900 homes, a third of them planned as affordable housing. The 2008 financial crisis had a profound impact on the normal development of the project causing the withdrawal of many developers, with only housing associations and bigger developers continuing afterwards. This delay and unexpected scenario let plots like the K1, where Marmalade Lane was erected, without any foreseeable solution. At this point, the city council opened the possibilities to a more innovative approach and decided to support a Cohousing community to collaboratively produce a brief for a collaborative housing scheme to be tendered by developers.
Involvement of users and other stakeholders
The South Cambridgeshire District Council, in collaboration with the K1 Cohousing group, ventured together to develop a design brief for an innovative housing scheme that had sustainability principles at the forefront of the design. Thus, a tender was launched to select an adequate developer to realise the project. In July 2015, the partnership formed between Town and Trivselhus ‘TOWNHUS’ was chosen to be the developer. The design of the scheme was enabled by Mole Architects, a local architecture firm that, as the verb enable indicates, collaborated with the cohousing group in the accomplishment of the brief. The planning application was submitted in December of the same year after several design workshop meetings whereby decisions regarding interior design, energy performance, common spaces and landscape design were shared and discussed.
The procurement and development process was eased by the local authority’s commitment to the realisation of the project. The scheme benefited from seed funding provided by the council and a grant from the Homes and Communities Agency (HCA). The land value was set on full-market price, but its payment was deferred to be paid out of the sales and with the responsibility of the developer of selling the homes to the K1 Cohousing members. Who, in turn, were legally bounded to purchase and received discounts for early buyers.
As relevant as underscoring the synergies that made Marmalade Lane’s success story possible, it is important to realise that there were defining facts that might be very difficult to replicate in order to bring about analogue housing projects. Two major aspects are securing access to land and receiving enough support from local authorities in the procurement process. In this case, both were a direct consequence of a global economic crisis and the need of developing a plot that was left behind amidst a major urban development plan.
Innovative aspects of the housing design
Spatially speaking, the housing complex is organised following the logic of a succession of communal spaces that connect the more public and exposed face of the project to the more private and secluded intended only for residents and guests. This is accomplished by integrating a proposed lane that knits the front and rear façades of some of the homes to the surrounding urban fabric and, therefore, serves as a bridge between the public neighbourhood life and the domestic everyday life. The cars have been purposely removed from the lane and pushed into the background at the perimeter of the plot, favouring the human scale and the idea of the lane as a place for interaction and encounters between residents. A design decision that depicts the community’s alignment with sustainable practices, a manifesto that is seen in other features of the development process and community involvement in local initiatives.
The lane is complemented by numerous and diverse places to sit, gather and meet; some of them designed and others that have been added spontaneously by the inhabitants offering a more customisable arrangement that enriches the variety of interactions that can take place. The front and rear gardens of the terraced houses contiguous to the lane were reduced in surface and remained open without physical barriers. A straightforward design decision that emphasises the preponderance of the common space vis-a-vis the private, blurring the limits between both and creating a fluid threshold where most of the activities unfold.
The Common House is situated adjacent to the lane and congregates the majority of the in-doors social activities in the scheme, within the building, there are available spaces for residents to run community projects and activities. They can cook in a communal kitchen to share both time and food, or organise cinema night in one of the multi-purpose areas. A double-height lounge and children's playroom incite gathering with the use of an application to organise easily social events amongst the inhabitants. Other practical facilities are available such as a bookable guest bedroom and shared laundry. The architecture of its volume stands out due to its cubic-form shape and different lining material that complements its relevance as the place to convene and marks the transition to the courtyard where complementary outdoor activities are performed. Within the courtyard, children can play without any danger and under direct supervision from adults, but at the same time enjoy the liberty and countless possibilities that such a big and open space grants.
Lastly, the housing typologies were designed to recognise multiple ways of life and needs. Consequently, adaptability and flexibility were fundamental targets for the architects who claim that units were able to house 29 different configurations. They are arranged in 42 units comprehending terraced houses and apartments from one to five bedrooms. Residents also had the chance to choose between a range of interior materials and fittings and one of four brick colours for the facade.
Construction and energy performance characteristics
Sustainability was a prime priority to all the stakeholders involved in the project. Being a core value shared by the cohousing members, energy efficiency was emphasised in the brief and influenced the developer’s selection. The Trivselhus Climate Shield® technology was employed to reduce the project’s embodied and operational carbon emissions. The technique incorporates sourced wood and recyclable materials into a timber-framed design using a closed panel construction method that assures insulation and airtightness to the buildings. Alongside the comparative advantages of reducing operational costs, the technique affords open interior spaces which in turn allow multiple configurations of the internal layout, an aspect that was harnessed by the architectural design. Likewise, it optimises the construction time which was further reduced by using industrialised triple-glazed composite aluminium windows for easy on-site assembly. Furthermore, the mechanical ventilation and heat recovery (MVHR) system and the air source heat pumps are used to ensure energy efficiency, air quality and thermal comfort. Overall, with an annual average heat loss expected of 35kWh/m², the complex performs close to the Passivhaus low-energy building standard of 30kWh/m² (Merrick, 2019).
Integration with the wider community
It is worth analysing the extent to which cohousing communities interact with the neighbours that are not part of the estate. The number of reasons that can provoke unwanted segregation between communities might range from deliberate disinterest, differences between the cohousing group’s ethos and that one of the wider population, and the common facilities making redundant the ones provided by local authorities, just to name a few. According to testimonies of some residents contacted during a visit to the estate, it is of great interest for Marmalade Lane’s community to reach out to the rest of the residents of Orchard Park. Several activities have been carried out to foster integration and the use of public and communal venues managed by the local council. Amongst these initiatives highlights the reactivation of neglected green spaces in the vicinity, through gardening and ‘Do it yourself’ DIY activities to provide places to sit and interact. Nonetheless, some residents manifested that the area’s lack of proper infrastructure to meet and gather has impeded the creation of a strong community. For instance, the community centre run by the council is only open when hired for a specific event and not on a drop-in basis. The lack of a pub or café was also identified as a possible justification for the low integration of the rest of the community.
Marmalade Lane residents have been leading a monthly ‘rubbish ramble’ and social events inviting the rest of the Orchard Park community. In the same vein, some positive impact on the wider community has been evidenced by the residents consulted. One of them mentioned the realisation of a pop-up cinema and a barbecue organised by neighbours of the Orchard Park community in an adjacent park. Perhaps after being inspired by the activities held in Marmalade Lane, according to another resident.
L.Ricaurte (ESR15)
Read more
->
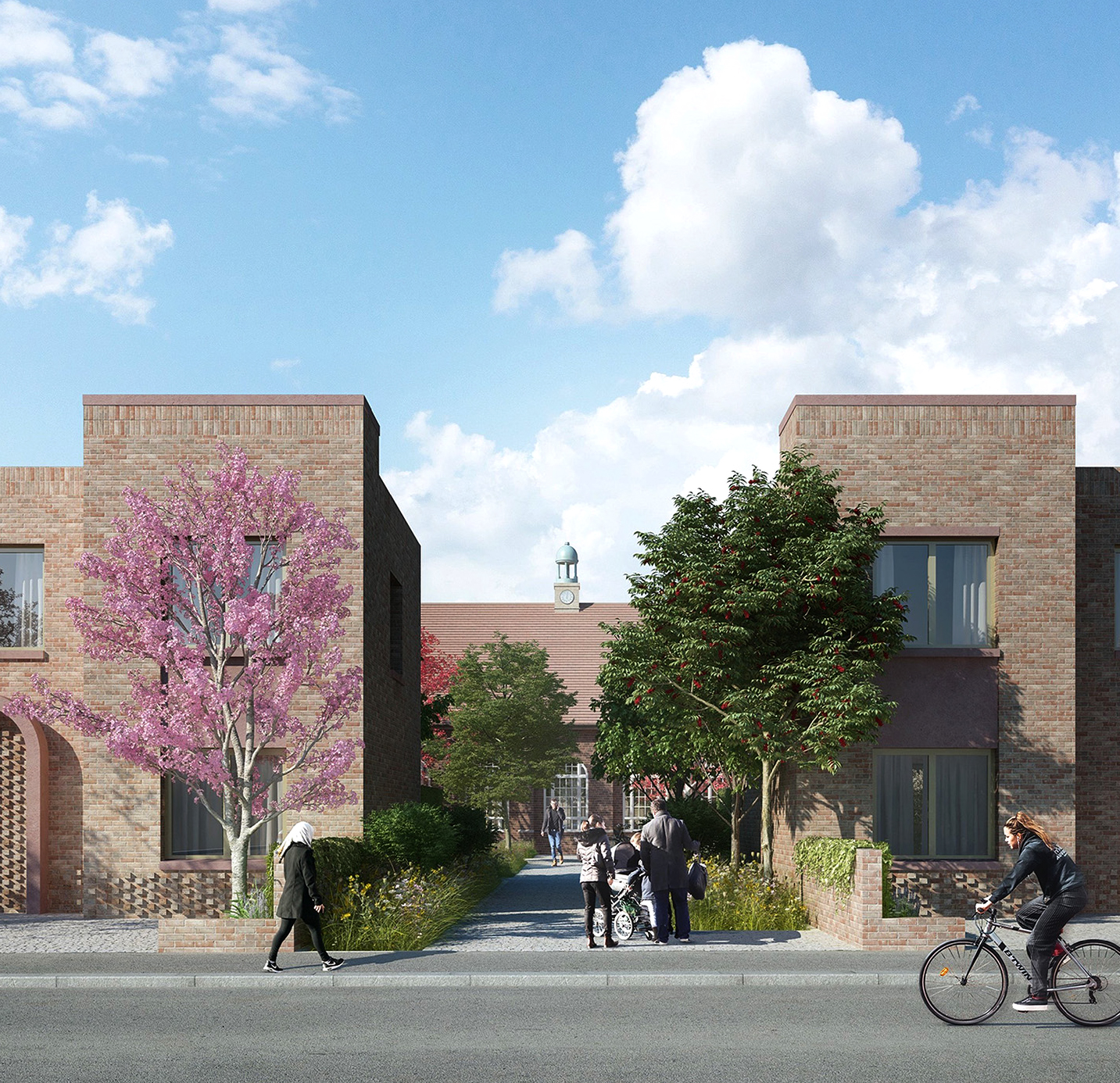

Deben Fields (Garrison Lane)
Created on 15-11-2023
The review and the analysis of this case is based on several sources of data including project design statements and reports (e.g., planning, architectural, transport, drainage, heritage, landscape, tenure, sustainability and energy), design drawings, planning application and the associated documentation, and archival records obtained from the designers and the East Suffolk planning portal. As well as conducting interviews with the actors involved in the project planning and design, namely the architects, energy system designers and sustainability specialists. Therefore, this review is structured to address various key aspects such as, design, construction, sustainability, community impact and cultural heritage.
1- Design statement
“The initial idea was a cricket pitch on the existing playing field and on the leftover land to develop 25 to 30 housing units. We saw an opportunity to connect the dots by connecting the school site into the cricket field and create better spaces and connectivity for the neighbouring communities […] through prober massing the site was optimised to increase the density to 61 housing units, maximising the views towards the park and generate best returns for the council […] that and investing in East Suffolk Council affordable housing scheme” (M. Jamieson, personal communication, June 13, 2023).
The Deben Fields development is located near the centre of Felixstowe in Suffolk, England (Figure 1). The site was previously occupied by Deben High School, which was built in 1930, surrounded by low-density semi-detached housing. In their design statement, TateHindle, the architects responsible for the project, articulate a design philosophy centred around the creation of an environmentally, socially, and economically sustainable neighbourhood. This vision places paramount importance on people, their lived experiences, and the integration of nature into the living environment (TateHindle, 2021, 2022). The site's redevelopment aligns seamlessly with East Suffolk Council's Housing Strategy, which emphasises the expansion of council-owned affordable housing through innovative and sustainable methods. To adhere to this strategy, the architect chose to preserve and repurpose existing structures on the site, including the school hall and its annexes. These buildings were meticulously retained, redesigned, and refurbished to serve as a new indoor public facility catering for both the current and anticipated population (ESC, 2021).
The project site is 3.89 hectares, of which 2.65 hectares is open green space (cricket pitch and park) and 1.36 hectares is allocated to residential development, with a net density of 53 dwellings per hectare and a total of 93 car parking spaces (61 for residential and 32 for leisure and community services) and 163 cycle spaces (HDA, 2022; TateHindle, 2021). The project is designed according to Passivhaus standards with airtight building envelopes and comprises 61 dwellings with 18 one-bedroom, 28 two-bedroom, seven three-bedroom and eight four-bedroom, spread across semi-detached houses, flats and maisonettes. From a tenure distribution point of view, 68 per cent are available at affordable rents, while the remaining 32 per cent are intended for open market sale (TateHindle, 2021). The average floor area of the housing units is 74.0 m², five per cent above the floor area requirement described by the Nationally Described Space Standard (HDA, 2022).
In terms of ownership, however, the aim is to deliver a ‘tenure neutral’ project, so there is no physical distinction between open-market, shared ownership and affordable rental housing. The tenure mix has been integrated throughout the site to ensure that the project delivers proper housing that meets the needs of the housing market. Figure 2 illustrates Deben Fields tenure distribution and housing typologies plans.
2- Construction
TateHindle's structural design statement outlines their goal of achieving a highly insulated façade construction. This was accomplished through the implementation of load-bearing double stud timber frame walls and load-bearing timber metal web beams at both floor and roof levels. The project uses Typical Passivhaus Foundations (TPFs) to minimise thermal bridging and achieve low U-values for the ground slab construction. Cradden (2019), however, explains that there are multiple challenges when using TPFs, such as soil conditions, material and geological properties (Cradden, 2019). To address these challenges, a shallow foundation method was chosen within the Red Crag Formation, a geological structure in south-eastern Suffolk defined by a basal pebble bed overlaid with coarse shell sand. This approach utilised the mini-pile technique, thereby bypassing the need for extensive and deeper excavations. In addition, Modern Methods of Construction (MMC) are used to maximise the use of off-site construction and achieve high levels of quality through factory-controlled assembly, reduce construction time, minimise noise pollution and construction waste, and reduce CO2 emissions (TateHindle, 2021).
3- Sustainability and energy
“The project has similar challenges to others […] with this project electrification and overheating were the main challenge […] so we did really want to simplify the forms to make it more Passivhaus compliant and cost-effective […] We started from rectangles; obviously you can then add and remove to create interest and increase efficiency” (sustainable design specialist, personal communication, July 20, 2023).
To achieve the planned outcomes of the economically, socially and environmentally sustainable neighbourhood, Deben Fields has set comprehensive objectives including: improving the well-being of residents, promoting pedestrian and child-friendly design, integrating passive design principles such as natural ventilation and daylighting, optimising construction costs and minimising waste through recycling and efficient use of materials, implementing monitoring systems for seamless building management, reducing sequestered carbon by reusing existing structures, promoting affordability as an overarching principle, adopting a fabric-first approach to reduce energy consumption and tackle fuel poverty, addressing future sustainability requirements, using renewable energy through photovoltaics to power communal areas and providing spaces that encourage social interaction such as areas for growing food and for play.
To translate design objectives into a practical design language, the project employed various approaches, as explained in the following subsections.
3.1- Architectural design and technology integration
The primary emphasis is placed on optimising the orientation of the buildings to harness passive solar gain effectively, thereby ensuring ample natural lighting and thermal comfort within indoor spaces (Figure 3). In pursuit of energy efficiency and to reduce overheating impacts, a simplified building form was devised. This involved implementing measures to minimise thermal bridging and establish an airtight building envelope, thereby reducing undesired energy losses. To emphasise the importance of insulation, sufficient provisions were made in the walls to allow for higher levels of thermal protection. A mechanical background ventilation with heat recovery system (MVHR) was used to create a well-ventilated and comfortable living environment. Furthermore, strategically positioned openings, balconies, entrances, sunshades, and shade pergolas contribute to a cohesive architectural language, fostering socially stimulating spaces while adhering to energy-efficient design principles in line with Passivhaus standards. The high-performance triple glazed windows have been carefully positioned and sized to allow natural cross ventilation. All of such techniques maximise control over the building envelope and reduce energy consumption.
3.2- Policy and standards
To achieve the desired sustainability goals, a combination of mandatory and voluntary policies and standards were introduced as part of the project design strategy. Firstly, the mandatory building regulations on sustainability, particularly Part L, which sets specific requirements for insulation, heating systems, ventilation and fuel consumption and aims to reduce carbon emissions by 31 per cent compared to the previous regulations. Secondly, the 'SCLP9.2' – a local planning initiative produced by East Suffolk Council to foment sustainable construction. The SCLP9.2 aims to achieve higher energy efficiency standards resulting in a 20 per cent reduction in CO2 emissions below the target CO2 emission rate, design the dwelling to use less than 110 litres of water per person per day, and encourage the use of locally sourced materials, with a focus on recycling and waste reduction (ESC, 2020, p. 9). Thirdly, the project adhered to Passivhaus standards and set a higher target by meeting higher sustainability standards in terms of energy efficiency, water consumption and material use. CGB Consultants – the sustainability specialist – clarified that with such combination of policies and standards, the dwellings could comfortably exceed the planning target for a 20 per cent improvement over building regulations, as simulated using calculations based on the Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP) (CGB, 2021).
4- Community and cultural heritage
In the early design phase, the design team developed a comprehensive communication plan that included public hearings and consultations with the community to inform planners of local needs, foster effective communication with project neighbours and obtain their feedback. However, the restriction of COVID-19 posed a challenge to the effective implementation of the original plan. In response, the architect and the City Council took alternative measures such as formal online consultations, monthly newsletters, social media updates, a website, public exhibitions, public notices, press releases, emails and letters. As a result, the project received critical feedback and concerns around impacts on nature, traffic, existing buildings, privacy, green spaces and alternative renewable energy sources.
Responding to the concerns raised, the project team developed a cycling and pedestrian strategy that introduces the concept of “green corridors", “rain gardens" and “play streets", while carefully allocated parking in line with the National Transport Strategy provides a green roof with photovoltaic panels. The community gardens, use the building structure as a privacy screen and integrate existing culture and heritage into the project (Figure 4).
Although the former Deben High School site is not nationally recognised as a historically significant building, it has become a local landmark with local significance and considerable architectural and historical value. Designed by Cecil George Stillman (1894–1968), a British architect known as a "pioneer of prefabrication" (Hinchcliffe, 2004). The proposed architectural language therefore draws on the existing buildings, particularly the school's building and assembly hall, which is considered the largest historic building on the site. The proposed pedestrian corridors also have helped to make the building more visible and put the assembly hall at the centre of the project (TateHindle, 2021).
5- Final reflections
This section highlights both the successful aspects and the potential areas for improvement arising from the review in the previous sections. This is by addressing the following questions:
What methodologies were deployed within Deben Field that can be classified as exemplifying ‘good' practise?
The proposed designs have looked beyond the initial requirements and original goals and proposed economically, socially and environmentally viable strategies and solutions. Jon Bootland (2011) explains that responsible housing design must adopt a rigorous design standard for low energy consumption, develop high-quality and affordable outcomes, and prioritise user comfort (Bootland, 2011). In response, the project has embraced higher design standards that go beyond mandatory building regulations and systematically addressed the challenges of engaging specialist services (including Passivhaus designers, ecology and biodiversity consultants, sustainable drainage designers and sustainability consultants) with a high level of expertise to provide the necessary technical feedback. In addition, current challenges such as electrification and overheating were proactively addressed by choosing simple architectural forms and integrating renewable energy sources.
While the project initially took a top-down approach, the community was actively involved in the early design phases through a variety of well-organised communication channels (as listed in section 5.4). The project team ensured that responses to planning notices were reviewed, analysed and incorporated into the architectural language of the project. For example, when neighbours raised privacy concerns, the building massing and layout were adjusted to form a privacy screen without compromising the number of dwellings provided. The project has also demonstrated an inclusive design approach that appeals to users of all ages (e.g., community garden and play street). In addition, the design has maximised the benefits of using brownfield sites and seamlessly integrated the existing infrastructure into the project layout, carefully considering the recycling and reuse of materials.
What are the vulnerabilities associated with Deben Fields?
Knox (2015) stated that the high construction costs of ‘green building’ are a common misconception for which there are insufficient studies (Knox, 2015). However, the study by Chegut et al. (2019) shows that “BREEAM – Excellent” certified buildings are 40 to 150 per cent more expensive to build and attributes these higher costs to specialised design costs, material selection, specialised labour and construction time (Chegut, Eichholtz, & Kok, 2019). The Deben Fields project adopted several sustainability features, such as special materials, green roofs and photovoltaic cells. However, it appears that the project has not conducted a thorough life-cycle cost analysis to determine the costs and benefits of these features and whether additional features are needed in the future.
Meanwhile, at the design level and to achieve the intended outcomes, the project complied with several standards and building codes, resulting in a complex and intertwined design structure that makes it difficult to apply the same strategies to other projects. From a sustainable urbanism perspective, density and diverse land use are often considered effective strategies for sustainable development (Carmona, 2021). Despite its central location, the project did not consider density and diversity of land use as a key strategy for its development. For example, the proposed project does not include any retail or commercial uses, and the nearest commercial services are 500 metres from the project (Figure 5).
The Deben Fields project is widely regarded as an example of ‘good practice’ in its field, as reflected in the number of awards it has won. However, in order to accurately assess the results of the project, it is essential to conduct additional post-occupancy studies. These studies will allow for a thorough evaluation of the project's features and provide valuable insights and potential areas for improvement. Another major factor contributing to its prominence is the use of numerous well-designed features. These features have improved the overall performance of the project and highlighted the novel techniques (e.g. play street, environmentally friendly materials, reducing overheating through massing). Therefore, it is crucial to undertake comprehensive documentation of all phases, steps and procedures taken during the design and construction of the project.
Acknowledgement
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to TateHindle Architects for generously providing the necessary data and information for Deben Fields. Special thanks go to Mike Jamieson for dedicating his time and expertise to discussing the project in detail. Additionally, I extend my appreciation to the anonymous interviewees who provided valuable insights into this case. Thank you all for your support and cooperation.
M.Alsaeed (ESR5)
Read more
->

Knight’s Walk (Lambeth's Homes)
Created on 26-07-2024
The review of this case study is structured to address aspects of architectural design, construction approach, and sustainability integration. The analysis draws on a range of data sources, including project design and access statements, sustainability statements, design drawings, planning applications, associated communications and archival records obtained from the planners, public records and the London Borough of Lambeth planning portal.
1. Design statement
The project site stretches to approximately 0.86 hectares, 84 residential units at a density of 215 dwellings per hectare are planned to be housed on the site. The surrounding areas are characterised by the prevalence of historic conservation areas. The site is located on the western side of the Cotton Garden Estate and is known for its public park and distinctive 22-storey Ebenezer, Hurley and Fairford towers. To the north is the Walcot Road Conservation Area with its three-storey terraced houses. To the east is Renfrew Roadside, which contains several listed buildings, including the Magistrates Court, the former Lambeth Fire Station and Workhouse (later converted to Lambeth Hospital) and what is now The Cinema Museum (Mae, 2017). Figure 1 illustrates the location of the project within the urban fabric of London.
In response to the unique characteristics and features of the site, the design team developed a comprehensive strategy to integrate the development. Firstly, the scale and massing have been carefully balanced in order to harmonize with the surrounding area. This is achieved through the use of graduated massing and a deliberate emphasis on the incorporation of open spaces and parks (Mae, 2017). Secondly, the existing transport and vehicular access has been maintained to avoid creating new routes. Thirdly, a car-free zone has been established, with the number of parking spaces on the site limited to eight, exclusively for residential units. Additionally, a number of bicycle parking bays have been installed to provide secure and convenient storage for cyclists. Fourthly, the "The Walk" concept has been implemented, offering a pedestrian route designed with human needs in mind, in an aim to promote connectivity between the site, parks, buildings, and existing public areas. This includes creating gateways and landmarks to enhance the sense of procession along the footpaths. Moreover, a balanced integration of soft and hard landscape elements was pursued to foster a sense of cohesive connectivity while preserving the site's architectural heritage (Mae, 2017). Figure 2 provides a comparative visual representation of the former site against the proposed design. Figure 2 provides a comparative visual representation of the former site against the proposed design for Knight’s Walk.
From a typological perspective, a total of 84 units have been developed, ranging in size from 54 square metres for the smallest units to 90 square metres for the largest. Phase one comprises 16 flats, including 10 one-bedroom flats, three two-bedroom flats and three three-bedroom flats. In contrast, phase two offers a broader choice with 15 one-bedroom flats, 38 two-bedroom flats and 15 three-bedroom flats.
With regard to architectural design, three key design considerations were identified as being of particular importance (HDA, 2022; Mae, 2017). The primary concern was the accessibility of the site for its residents, with particular attention paid to the needs of senior citizens and those with special requirements. This emphasis is particularly pronounced in Phase One, where the majority of units have been designed to meet both the Building Regulations Part M (which provides guidance on access to and use of buildings, including facilities for disabled occupants and easy movement through a building), and the prescribed national standards for accessible spaces (Mae, 2017). Secondly, the efficient use of space was prioritised, with the use of simple and clean architectural lines to optimise the functionality within each unit and the circulation areas. Thirdly, the well-being of residents was a significant consideration, with each unit featuring a terrace overlooking the surrounding green spaces and parks. The overall distribution of flats in both phases is shown in Figure 3.
2. Construction
In terms of construction methods, the project adopts a fabric-first approach that focuses on improving the properties of the building fabric, with the objective of optimising thermal performance, airtightness and moisture management. This approach is intended to reduce the necessity for additional mechanical or technical solutions, thereby achieving enhanced energy efficiency and comfort (Eyre et al., 2023). In addition, project planners have incorporated supplementary measures to improve construction processes (Mae, 2017). These include using a reinforced concrete structure in locations prone to thermal bridging, while avoiding cores as the primary structural support system. Furthermore, a strategy to rationalise the building’s "form factor" ensures a coherent visual progression of the building mass whilst mitigating thermal impacts such as overheating on the overall building envelope. Secondly, a balanced glazing ratio has been implemented to reduce direct thermal impacts, with the additional benefit of providing resistance to thermal mass. The use of light-coloured materials also serves to reduce the heat island effect and thermal conductivity between the exterior and interior of the building. Finally, the use of a cantilevered method, particularly in building extensions, reduces thermal bridging while improving the overall aesthetics of the structures.
3. Sustainability and energy
Several methods to promote sustainability have been integrated into the building’s envelope. The project follows the three-point model known as the "energy hierarchy", which is based on the principles of "Be Lean", "Be Clean", and "Be Green". “Be Lean” emphasizes the planning and construction of buildings that consume less energy. "Be Clean" focuses on efficiently providing and consuming energy, while "Be Green" aims to meet energy needs through renewable sources (Muralidharan, 2021).
3.1. Energy and carbon strategy
In line with energy hierarchy models, the project's energy strategy focuses on the building envelope and incorporates high-performance standards recommended by Passivhaus to optimise building mass and thermal boundaries. In addition, provisions have been made to future-proof the buildings by providing provisional spaces for future connection to planned district and central heating systems. Efforts to reduce carbon emissions centre on establishing accurate baseline emissions using the Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP), implementing passive measures such as natural ventilation and high-efficiency appliances, and reducing reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation through the use of photovoltaic cells as a secondary energy source. As a result, the buildings have achieved a 35 per cent reduction in carbon emissions compared to local regulations and similar developments (Mae, 2017; TGA, 2017).
3.2. Overheating strategy
Managing the risk of overheating has become an essential consideration in the design and construction of housing in the UK (Sameni et al., 2015). The quality of the indoor environment in any dwelling, particularly in summer, is vulnerable to excessive solar heat gain which is accentuated by the lack of rapid ventilation measures. To mitigate these challenges, the project's overheating strategy minimises internal heat generation through energy-efficient design and reduces heat gain through careful orientation, shading, windows, and insulation. Passive ventilation measures, such as natural cross-ventilation and fixed external shading, are also utilised. In addition, primary heating pipework is carefully planned to minimise losses, particularly when installed within the dwellings (TGA, 2017).
3.3. Policy and standards
The project has been developed in accordance with a complex network of interrelated policies and standards at the national, regional and local levels, in addition to mandatory national sustainability guidelines. Notably, Building Regulations Part L, which sets out specific requirements for insulation, heating systems, ventilation and fuel use, and aim to reduce carbon emissions by 31 per cent compared to those of previous regulations. Knight's Walk introduced a new layer of mandatory requirements, designated as "regional" guidelines. These guidelines are specific to the Greater London area and serve as a reference for all developments. In addition to fulfilling the national and regional regulations, the project had to comply with the requirements set forth by the local councils. Furthermore, the developer's requirements, known as Lambeth's Housing Design Standards function as a clarifying framework, outlining the pertinent policies at the national and regional levels.
As a result, the project has comfortably achieved an energy rating of B (based on the Standards Assessment Procedure calculations), with the potential to progress to an A rating. The project has developed a multi-level sustainability strategy and architectural language that considers climate, environment, and local needs, focusing on energy and carbon reduction. These strategies include encouraging active travel, increasing biodiversity and implementing adaptations to mitigate the effects of climate change through a drainage strategy and incorporating SuDS and tree planting. In addition, each flat has been fitted with mechanical ventilation with heat recovery, providing a constant supply of fresh, filtered air even when the windows are closed. All apartments are also equipped with energy-saving electrification systems to minimise electricity consumption (HDA, 2022).
4. Reflections
The section highlights both the successful aspects and the potential areas for improvement identified in the previous sections by addressing the following questions:
What methodologies were deployed within Knight’s Walk that can be classified as exemplifying ‘good’ practise?
The comprehensive assessments conducted by the designers, covering a wide range of intervention areas, facilitated the formulation of a responsible phasing strategy that mitigated the social, economic, and environmental risks associated with large-scale development projects. The early provision of alternative, well-built housing for tenants who were displaced has fostered robust collaboration between developers, designers, and local communities.
The project was developed in accordance with widely recognised accessibility standards, including compliance with Building Regulations Part M. A comprehensive assessment framework was employed to measure the quality of outcomes in line with national, regional, and local policies. In order to facilitate the adoption of improved energy efficiency strategies, consultation was undertaken with specialists versed in Passivhaus design standards. As a result of this consultation, it was determined that no additional standards were required. These strategies included the implementation of passive measures, such as massing, orientation, and material selection, complemented by high-efficiency mechanical ventilation systems, photovoltaic cells, energy-efficient appliances and well-insulated façade designs. As a result, the project achieved a Class B environmental performance during the operational phase and a diminished average national CO₂ emission for residential buildings by 80 per cent. The project's carbon production averaged 0.7 tonnes of CO₂ per year, with primary energy consumption ranging from 42 to 58 kilowatt hours per square metre (kWh/m2) (DLUHC, 2021).
What are the potential weaknesses inherent to Knight’s Walk?
Notwithstanding the robust practices that were put in place, several risks were identified, particularly in relation to the design approach that was selected. Although the fabric-first approach is regarded as a fundamental tenet of sustainable construction, it has not been without its detractors. A significant concern is the long-term variability in the performance of fabric-first buildings, which is contingent upon factors such as maintenance practices, occupant behaviour and climate fluctuations. Inadequate construction quality or maintenance practices can result in the deterioration of energy efficiency gains over time, underscoring the need for continuous monitoring and maintenance (Eyre et al., 2023). This could consequently result in a considerable increase in operational costs, thereby jeopardising the objective of housing affordability over the long term. Furthermore, buildings with high insulation using the fabric-first approach may be susceptible to overheating during the warmer seasons in certain climates, particularly if passive cooling strategies are inadequately integrated into the design (Eyre et al., 2023). This can lead to additional energy consumption for cooling purposes and counteract efforts to achieve highly efficient energy.
M.Alsaeed (ESR5)
Read more
->