Design Activism
Area: Community participation
Activism as a term illustrating the urban phenomena of citizen mobilisation and direct action(s) towards political, social and environmental change that emerged during the early 20th century (Hornby, 1995). Seen also as a “means of overcoming alienation” (Graeber, 2009, p. 231), numerous forms of activism were significantly influenced by the Situationist International, which advocated the creation of spontaneous, subversive “situations” as a response to the increasing commodification and individualisation of everyday life (Debord, 1992). In this sense, activism can be seen as a means to repoliticise and breathe meaning into an everydayness[1] characterised by passive bystanding and to create instances where people are able to redefine their agency as urban dwellers and political subjects[2] (Graeber, 2009).
Design activism has been defined as any practice that “draws attention to change in the context of design through positive experimentation and action, introducing a designerly way of intervening into people’s lives” (Mallo et al., 2020, p. 102). According to Markussen (2013), it reflects the role and potential of various design fields in (1) promoting social change, (2) express values and beliefs in a tangible way and (3) question the systemic constraints that impact people’s daily lives. Due to the rising levels of precarity, caused by the increasing neoliberalisation of politics, policies and everyday life on a global scale (Brown, 2015), design activism in architecture and urban planning (often associated with DIY urbanism) has been gaining traction over the past decades among scholars and practitioners, as a transformative means of renegotiating the role of architecture and planning within the mechanisms of spatial production, as well as reasserting citizens’ agency over their urban environment (Markussen, 2023).
Design activism in architecture may operate both symbolically, in order to illustrate and highlight socio-spatial injustice (e.g. Santiago Cirugeda’s[3] insect house) and pragmatically, through the creation (disruptive) of spatial configurations “across a number of people and artefacts” (Mallo et al., 2020, p. 102), in a direct-action manner, with the aim of improving people’s livelihoods. Direct action can be “any collective undertaking that is both political in intent and carried out in the knowledge that it might be met with hostility […]” (Graeber, 2009, p. 359). The element of direct action emphasises both the immersiveness, the astute responsiveness to actual circumstances and the moving away from a general, pre-defined, vague and ultimately co-opted “social good” (Fuad-Luke, 2017), towards a more situated understanding of urban space and people’s needs. Collaborative, “unalienating” acts of urban creativity, connect (architectural) design activism to practices such as participatory design, co-creation and concepts like spatial agency, all of which employ different means to reassert urban dwellers’ position as crucial and indispensable parts in decision-making processes.
Scholarly criticisms towards design activism focus on its temporal and experimental nature, which renders quantifying and crystallising the long-term effect on urban landscapes and dwellers difficult (Mallo et al., 2020). Arguably, its situatedness may also pose an obstacle towards the creation of any universal toolkit, strategy or course of action that could be transferable to different contexts and employed to tackle varying circumstances. It remains, however, a vital phenomenon towards fostering agency and a shared sense of citizenship and camaraderie, repoliticising architecture and planning practices, as well as nurturing a culture of working (ant)agonistically towards incremental change in the cities, one intervention at a time.
[1] Georg Simmel described and everydayness where bystanding and lack of concern are primary “symptoms of what he called “blasé attitude”. This term emerged so as to illustrate the overstimulating everydayness of the sprawling capitalist metropolises of the late 19th - early 20th century that renders individuals idle (“The metropolis and mental life”, first published in 1903). Contrary to Simmel, Michel de Certeau posits that individuals operating under imposed regulations and conditions, may find ways to interpret them differently, even subvert them, often by unconsciously utilising systems of socio-cultural references that may deviate from the dominant one(s) (De Certeau, 1984).
[2] “A subject develops an understanding of itself as a political subject only by executing decisive political actions” (Calcagno, 2008)
[3] More information on this project can be found here: https://unprojects.org.au/article/architecture-on-the-fringes-of-legality-santiago-cirugeda-kyohei-sakaguchi/ & here: https://www.cca.qc.ca/actions/fr/node/82
References
Brown, W. (2015). Undoing Democracy - Neoliberalsm’s Remaking of State and Subject. In Undoing the Demos, Neoliberalism’s Stealth Revolution (pp. 17–45). Zone Books.
Calcagno, A. (2008). Alain Badiou: The event of becoming a political subject. In Philosophy and Social Criticism (Vol. 34, Issue 9, pp. 1051–1070). https://doi.org/10.1177/0191453708098537
Debord, G. (1992). Society of the spectacle. Rebel Press.
De Certeau, M. (1984). The Practice of Everyday Life. University of California Press.
Fuad-Luke, A. (2017, January 4). Design Activism’s teleological freedoms as a means to transform our habitus. http://agentsofalternatives.com/?p=2539
Graeber, D. (2009). Direct Action: An ethnography. AK Press. www.akpress.org.
Hornby, A. S. (1995). Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (J. Crowther, Ed.; 5th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Mallo, D., Tardiveau, A., & Parsons, R. (2020). Design activism: Catalysing communities of practice. In arq: Architectural Research Quarterly (Vol. 24, Issue 2, pp. 100–116). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1359135520000184
Markussen, T. (2013). The Disruptive Aesthetics of Design Activism: Enacting Design Between Art and Politics. Design Issues, 29(1), 38–50. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1162/DESI_a_00195
Markussen, T. (2023). Bursting housing bubbles and the agency of urban design activism. In The Routledge Handbook of Urban Design Research Methods (pp. 73–82). Taylor and Francis. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003168621-9
Created on 13-02-2024 | Update on 23-10-2024
Related definitions
Co-creation
Area: Community participation
Created on 16-02-2022 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Participatory Approaches
Area: Community participation
Created on 17-02-2022 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Community Empowerment
Area: Community participation
Created on 03-06-2022 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Urban Commons
Area: Community participation
Created on 14-10-2022 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Direct Action
Area: Community participation
Created on 18-06-2024 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Housing Quality
Area: Design, planning and building
Created on 14-10-2024 | Update on 23-10-2024
Read more ->Related cases
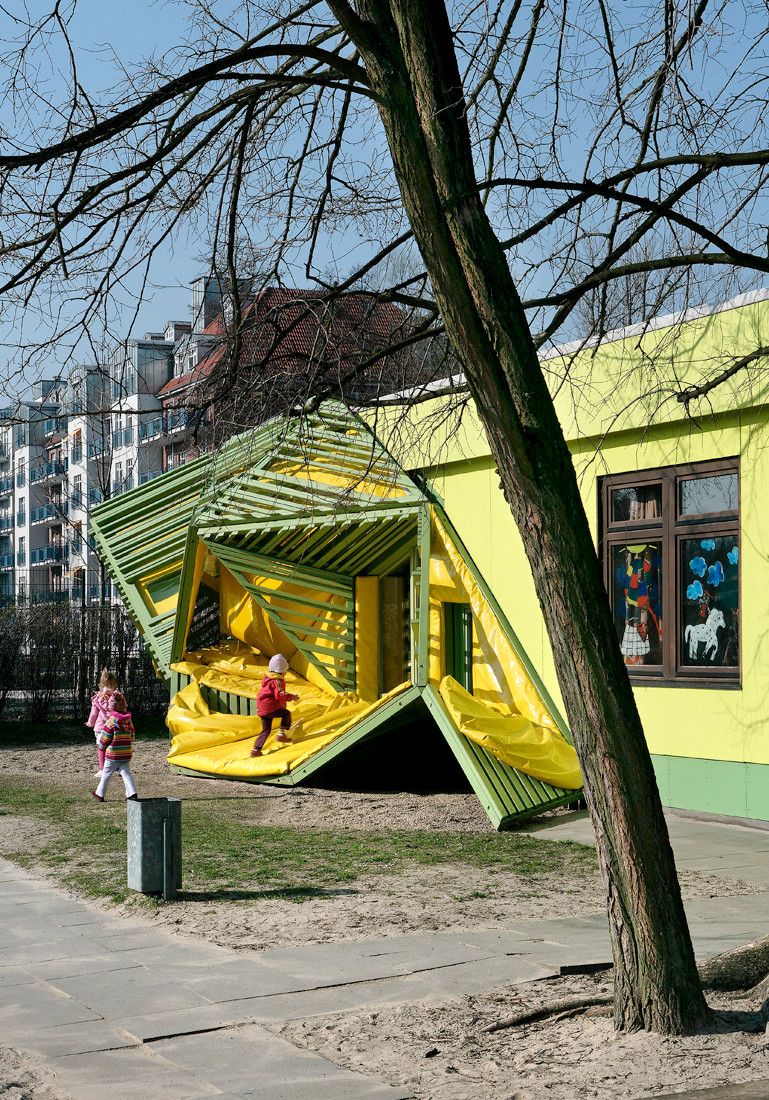

Die Baupiloten Berlin
Created on 29-07-2024
Related publications
No entries