The Elwood Project, Vancouver, Washington
Created on 09-06-2022 | Updated on 25-01-2024
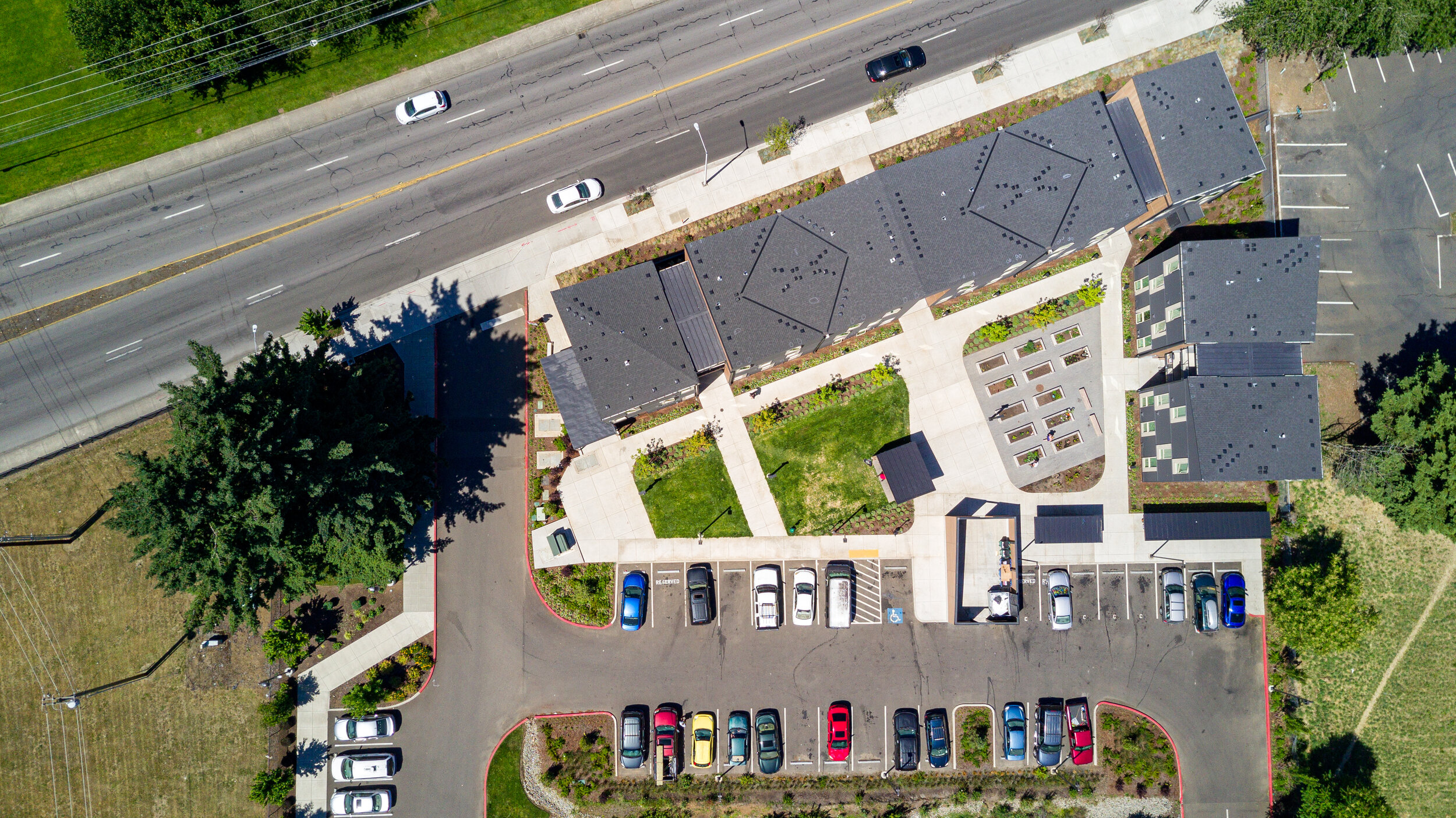
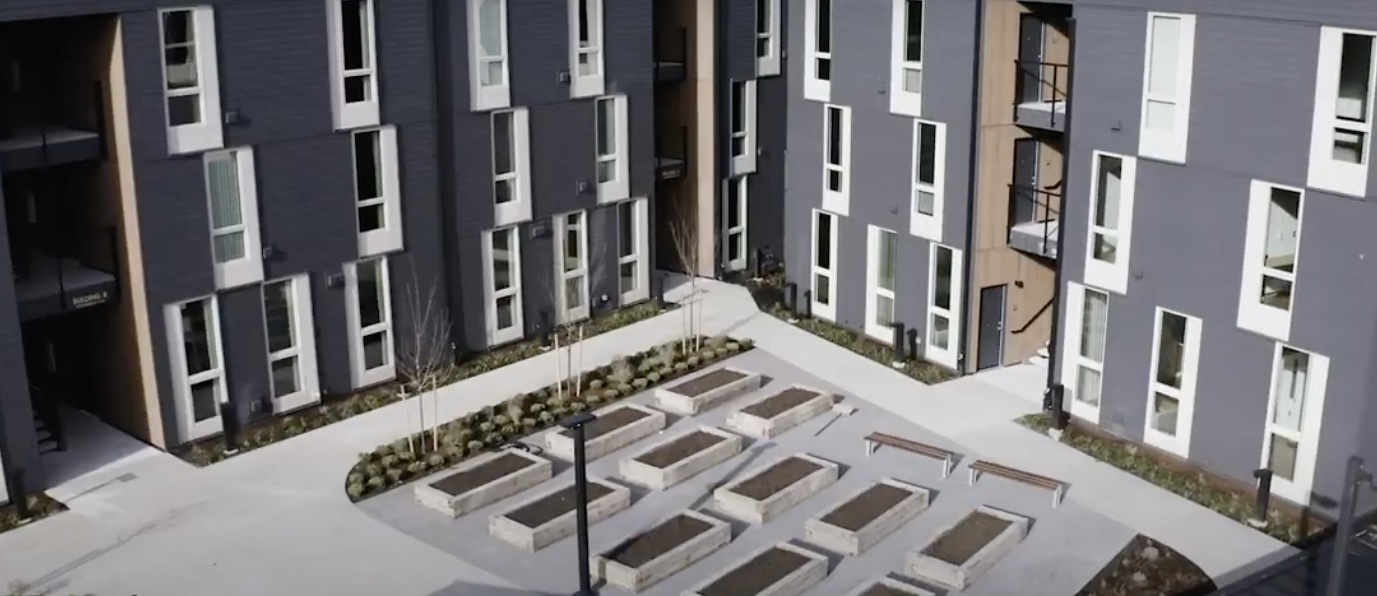
The Elwood Project is an affordable housing community project owned by the Housing Initiative, LLC, which is a subsidiary of Council for the Homeless in Clark County, WA. It consists of four three-storey buildings with forty-six apartment homes. Half of these homes are designed for homeless people, considering their special physical and behavioural health needs (Otak, 2022). Elwood is a socially relevant example of permanent supported housing. Brendan Sanchez and his Access Architecture team used trauma informed design (TID) principles for the entire building to serve and empower the residents. Numerous partners contributed to the success of this project: Access Architecture, CDM Services, City of Vancouver Affordable Housing Fund, Clark County, Hunt Capital Partners, Otak, Inc., Se Mar – Community Services Northwest, TEAM Construction, Vancouver Housing Authority, Washington State Finance Commission (Council for the Homeless, 2022).
Architect(s)
Access Architecture
Location
Vancouver, Washington 6317 NE Fourth Plain Boulevard in Vancouver
Project (year)
2021
Construction (year)
-
Housing type
permanent supporting housing, three-storey buildings with forty-six apartments
Urban context
-
Construction system
vintage wood (fiber cement cladding), wooden/concrete/steel frame, off-site industrialised construction
Status
Built
Description
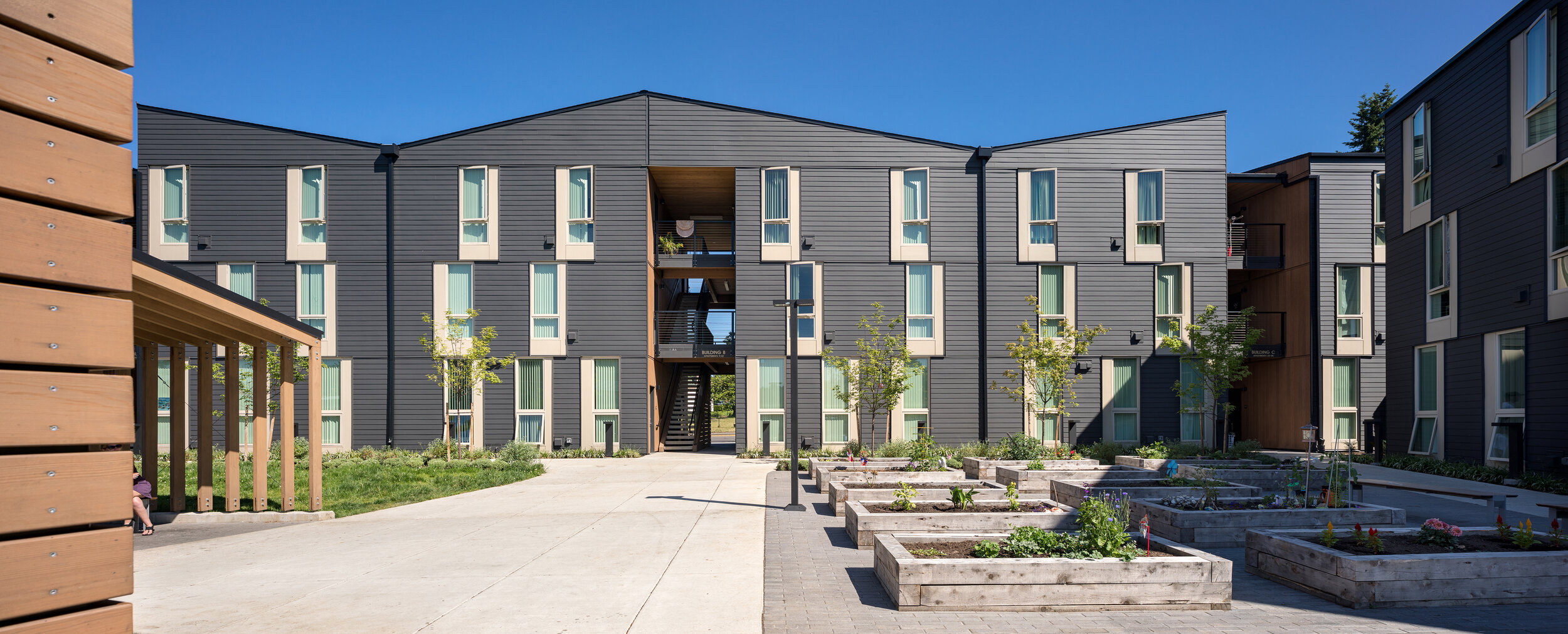
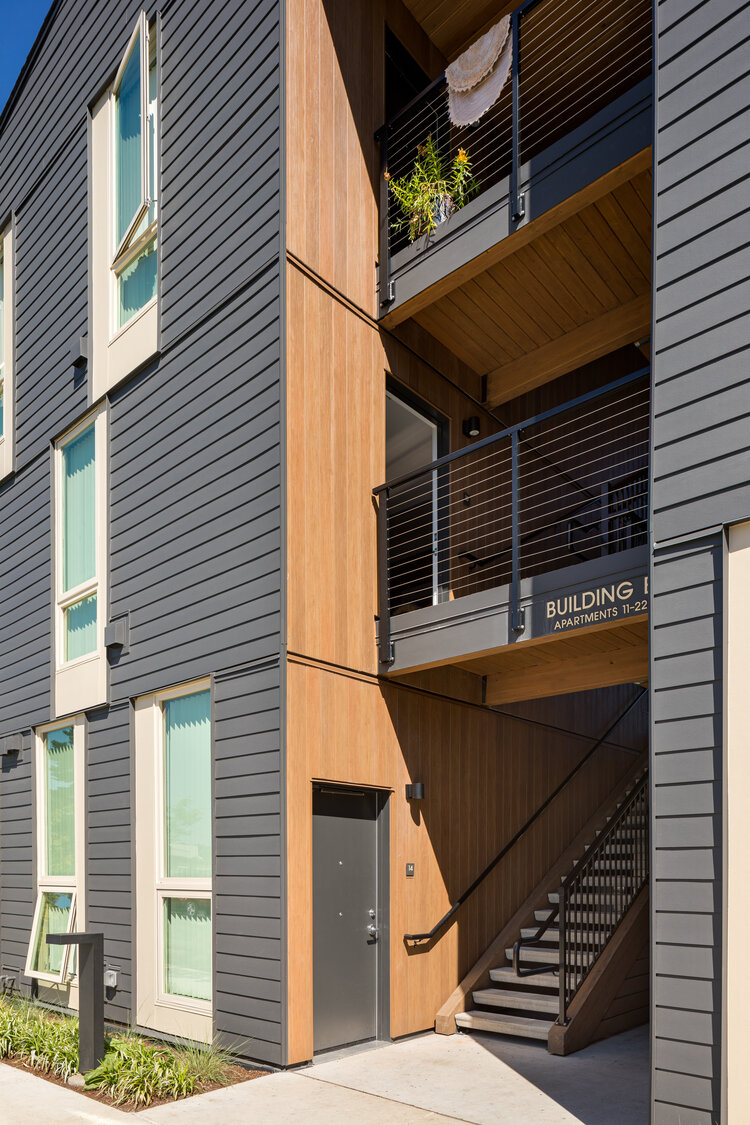
The Elwood Project is an affordable housing development and includes forty-six apartments and supportive housing services provided by Sea-Mar Community Services. All apartments are subsidised through the Vancouver Housing Authority, so that tenants pay thirty-five percent of their income towards rent, according to public housing designation. There are garden-style apartments to allow residents to choose when and where to interact with neighbours. Units are 37 sq. m. with 1 bedroom. These apartments are fully accessible and amenities include a community room, laundry room, covered bike parking, and outdoor courtyard with a community garden (Housing Initiative, 2022).
This case highlights the benefits of trauma informed design (TID) in the supportive housing sector. These homes were built using concepts of open corridors, natural light, art and nature, colours of nature, natural materials, design with commercial sustainability, elements of privacy and personalization, open areas, adequate and easy access to services. With these thoughtful techniques, Elwood offers socially sustainable help for vulnerable people (people with special needs, homeless, formally homeless) and for the new “housing precariat”.
The Elwood project is a good example of combining private apartments with opportunities for community living, where services and facilities management contribute to the well-being and stability of dwellers. What makes this project especially unique is that it does not look like affordable housing. As Brendan Sanchez concluded, people think that it “looks like really nice market rate upscale housing”, which is empowering, because people in general “deserve access to quality-built environment and healthy indoor interior environments”. Access Architecture did not design it as affordable housing, they just “designed it as housing” (Access Architecture, 2022).
Affordability aspects
The Elwood affordable housing community project is in a commercially zoned transit corridor. Existing planning regulations did not allow building permits in this area. Elwood is the first affordable housing development in the city of Vancouver that has required changes to the city’s zoning regulations. As a result of these changes, other measures have been adopted to promote affordable housing in the community. Under the city's previous building regulations, it was simply not possible to obtain a building permit. The Affordable Housing Fund helped developers to undertake this project and provided tenants with budget friendly housing options (Otak, 2022).
Now, thanks to the Elwood project, there are ongoing talks at the Board of the Planning Commission of Elwood Town to get construction permits for similar projects. As the council stated, “it is on the horizon for all towns to have affordable housing” (Elwood Town Corporation, 2022). Although the population of the area is small, it is estimated that in the coming years the need for more affordable housing units will increase. Previously, permitted uses were limited to C-2 (general commercial, office and retail) and C-3 (intensive service commercial) zoning uses (e.g., gas station, restaurant, public utility substation). Currently, the members of the town council together with other stakeholders are negotiating new plans for affordable housing in the area. With the help of the community, they are striving to harmonise the legal, political, financial and design aspects and work on a general plan that includes the construction of multi-family affordable dwellings. In addition, the ultimate goal is to further modify zoning regulations to incorporate tax advantages for social housing.
Sustainability aspects
It is a highly energy efficient building as it meets the minimum requirements of the Evergreen Sustainable Development Standards (ESDS), which include requirements for low Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) content, water conservation, air sealing, and reduction of thermal bridges. It also meets the Green Point Rated Program requirements. The building materials are bamboo, cork, salvaged or FSC-Certified wood, natural linoleum, natural rubber and ceramic tile. There are no VOC adhesives or synthetic backing in living rooms, and bathrooms (Otak, 2022).
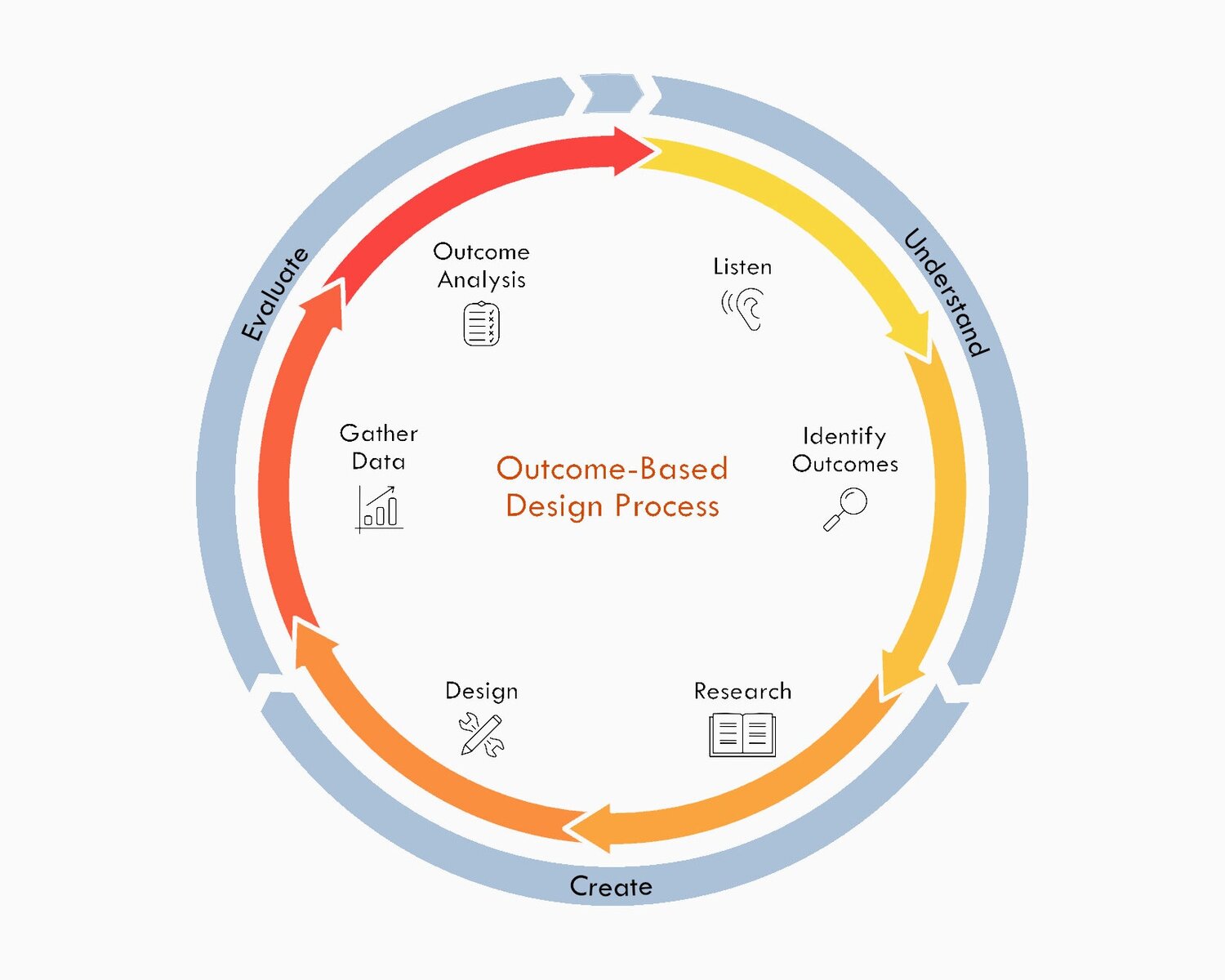
Design
Access Architecture used an outcome-based design process during the development of this project.
The outcome-based design process considers TID principles to lower barriers among tenants and minimize stigma of receiving services. Brendan Sanchez from Access Architecture highlights that TID is a kind of design that is “getting a lot more attention now that people understand it more. It applies in this project, and we’re also just finding that it doesn’t have to be a certain traumatic event we design for. It can also be a systemic problem — we all have our own traumas we’re working through, especially after the events of the pandemic last year. So Access likes to focus on how we can create healing spaces in this kind of design.” (Nichiha, 2022)
As Di Raimo et al. (2021) wrote, trauma informed approaches can be adopted by a wide range of service providers (health, social care, education, justice). In this case, Sea Mar-Community Services Northwest’s Foundational Community Support provides guidance for tenants with the help of case managers. Such partners can help with professional and health objectives. CDM Caregiving Services helps (or offer assistance) with daily tasks from cooking to cleaning and hygiene. Finally, Vancouver Housing Authority members help with anything they can, so that tenants would not feel themselves alone with their problems (Nahro, 2022).
Elwood offers informal indoor and outdoor spaces which provide a relaxed atmosphere in a friendly milieu. In this building, TID suits the resident’s needs. The building was planned with the help of potential residents and social workers, so that a sense of space and place would provide familiarity, stability, and safety for those who are longing for the feeling of place attachment.
Alignment with project research areas
The Elwood project as a case study represents how the three research areas of RE-DWELL are necessarily connected and interrelated whenever the aim of the development project is to provide sustainable and affordable housing.
According to the architects of Access Architecture, this case is a good example of informed design and community engagement (Access Architecture, 2022a). It was crucial for the creators of the project to foster meaningful connections among participants during the planning and building processes, and to provide future residents with the chance to connect with each other and with their environment. Therefore, this project exemplifies the need to align design, planning and building and community participation.
Elwood utilized trauma-informed design, which positively influences social, environmental, and economic sustainability. In general, the use of outcome-based design helped the developers to reach vulnerable groups, listen to their needs and include their voices and wishes in the planning and design outcomes. As a result, there was an accent on dignity, independence, empowerment, environmental control, community, healing environments, privacy, safety, affordability, and security.
This case is also characterized by social and economic inclusion and demonstrates a strong alignment with policy and financing too. To respond to the need for social housing it was necessary to change the existing legal framework. The greatest challenge was to build a new financing network with the participation of authorities and stakeholders from different sectors. Policy makers and investors functioned as key actors. The Washington State Finance Commission and the City of Vancouver Affordable Housing Fund had a crucial role as well.
Future projects can learn from this community effort. Case specific solutions and ordinances can be investigated, to analyse how the rules of zoning and tax benefits could be changed or shaped. In sum, Elwood is a constant source for learning (e.g., understanding legal or financial complexities, analysing community involvement, investigating the current operation of the facility and estimate the positive impacts of TID).
* This diagram is for illustrative purposes only based on the author’s interpretation of the above case study
Alignment with SDGs
Elwood responds to the following Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
1. No poverty: End poverty in all its forms everywhere (Targets: 1.3; 1.4)
This supporting housing option provide affordable (below market level) prices and above average quality and energy efficient solution for the given price. Having an affordable and secure rent increases the purchasing power of the tenants in line with the proper implementation of national social protection systems and measures for all. There is a special focus on the poor and on vulnerable men and women, providing equal rights to basic services. (Highly related)
3. Good health and well-being: Promote well-being for all at all ages (Target: 3.4)
Tenants at Elwood can feel part of a community, where their living conditions can be described with the following words: adequate, quality, accessible and healthy. The well-being of the tenants is one of the main goals of the project. (Highly related)
4. Quality Education: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all (Target: 4.3)
This project can offer a basis for tenants who would like to have a formal or further education despite their vulnerable situation. Tenants have equal access to affordable housing and quality education. (Moderately related)
6. Clean Water and Sanitation (Target: 6.1; 6.2) and 7. Affordable and clean energy: Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all. (Targets: 7.1; 7.2; 7.3 )
Elwood was designed in line with SDG6 and SDG7, with water conservation, air sealing, and a reduction of thermal bridges. It also meets the Green Point Rated Program requirements in line with providing access to safe and affordable drinking water and access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all. The Evergreen Sustainable Development Standards (ESDS), ensure access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. (Highly related)
8. Decent work and economic growth: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all (Targets: 8.3; 8.5;)
A long-term goal is to reintegrate residents of Elwood in society and the workforce, and to support productive activities and decent job creation (Moderately related)
10. Reduced inequalities: Reduce inequality within and among countries (Targets: 10.2; 10.3; 10.4)
The whole idea of the Elwood project resonates with the aim to help on traumatized groups, and to prevent re-traumatization. More generally, to empower and promote social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status. Another important goal is to eliminate discriminatory laws, policies and to adopt social protection policies. (Highly related)
11. Sustainable cities and communities: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable. (Targets: 11.1 ; 11.3 ; 11.5)
Elwood offers a safe environment for the tenants, and it can improve the quality of the neighbourhood (“hopeful urbanism”) too. It also aims to ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums. Meanwhile it respects the process of inclusive and sustainable urbanization and targets capacity upgrade for participatory, integrated, and sustainable human settlement planning and management. With its pro-poor focus and work with vulnerable groups it also contributes towards the specific target of 11.5. (Highly related)
13. Climate action: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. (Targets: 13.2 ; 13.3)
Elwood is characterized by climate smart planning, together with awareness raising, utilizing both individual and institutional capacity. (Highly related)
References
Access Architecture (2022a). https://www.access-arch.com/about
Access Architecture (2022b). https://www.access-arch.com/the-elwood
Bollo, C. & Donofrio, A. (2021) Trauma-informed design for permanent supportive housing: four case studies from Seattle and Denver. In Housing and Society, DOI: 10.1080/08882746.2021.1989570
Di Raimo, A., Petrillo, M., & Thomas, M. (2022). Why resilient communities need trauma-informed care the case for trauma informed design for resilient cities. In M. Carta, M. R. Perbellini, & J. A. Lara-Hernandez (Eds.), Resilient Communities and the Peccioli Charter: Towards the Possibility of an Italian Charter for Resilient Communities (pp. 213-222). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85847-6
Elwood Town Corporation (2022). https://www.elwoodtown.com/documents/415/PCminutes_5-17-22.docx__1_.pdf
Housing Initiative, LLC (2022). https://housinginitiative.net/completed-projects/
Nahro (2022). https://www.nahro.org/journal_article/vancouver-housing-authority-provides-permanent-supportive-housing-to-homeless/
Nichiha (2022). https://www.nichiha.com/docs/Nichiha-CaseStudy-Trauma-Informed-Design.pdf
Related vocabulary
Affordability
Community Empowerment
Social Sustainability
Area: Design, planning and building
Created on 03-06-2022
Read more ->Area: Policy and financing
Created on 21-04-2023
Read more ->Area: Community participation
Created on 03-06-2022
Read more ->Area: Community participation
Created on 03-06-2022
Read more ->Blogposts

Clashing Vulnerabilities
Posted on 13-02-2023
Secondments
Read more ->