Exploring the Panorama of Barcelona's Urban Commons and the Dynamic State Relationships
Posted on 22-01-2024
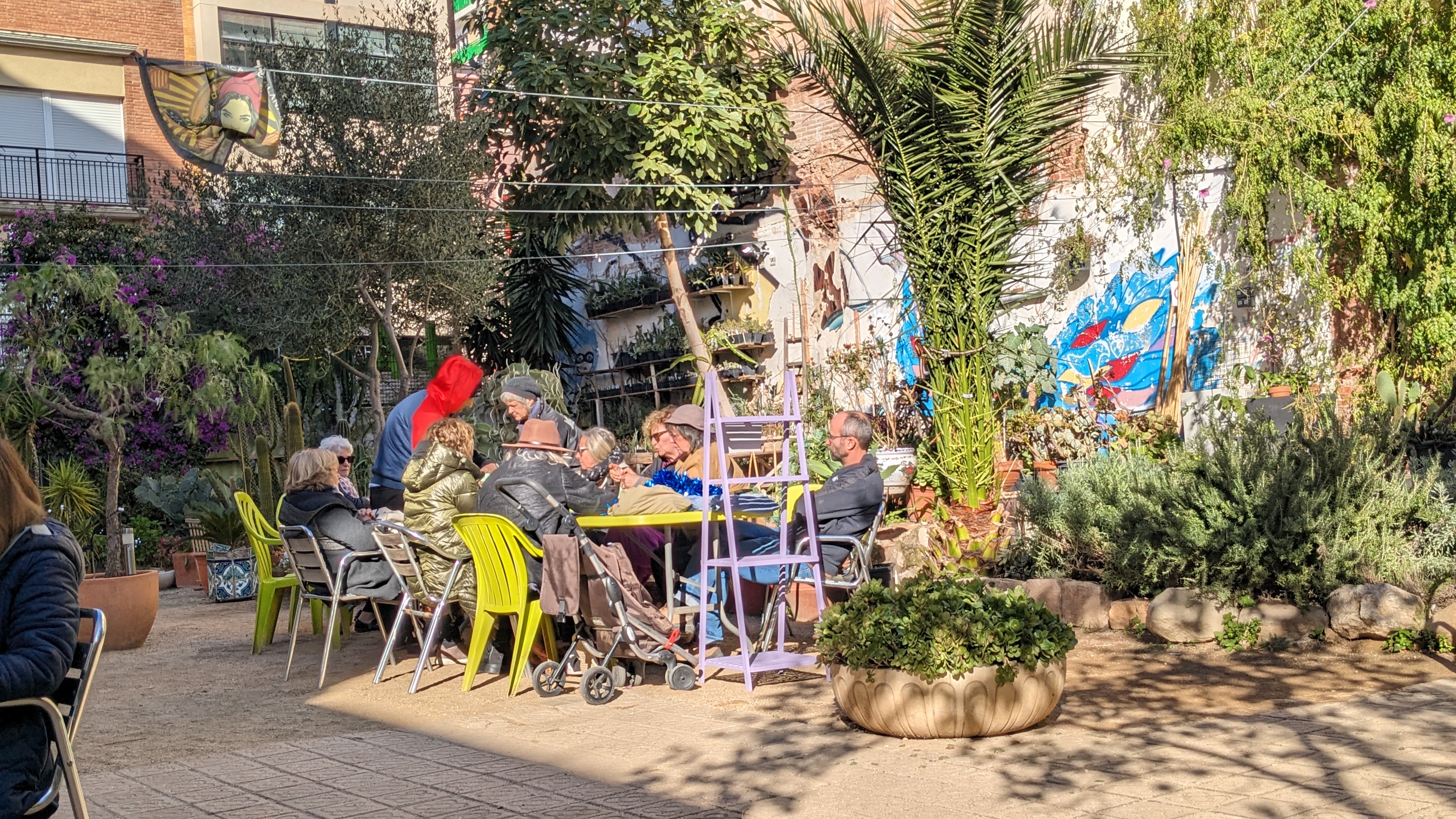
During the first days of 2012 the residents around Encarnació 62-64 in the neighbourhood of Grácia in Barcelona, gathered outside the -up until then- nuns’ convent due to the sound of excavators tearing down the entire 1900’s building in just 3 days. Apart from the building, the site preserved an 800 square meter garden with pergola, century-old palm trees and fruit trees, house of several bird species, such as parrots, blackbirds, doves, robins or sparrows.
Word spread that the site had been sold to a real estate company with plans to construct a six-storey parking lot. The residents of the streets Encarnació, Sant Lluis and the Associació Veïnal Vila de Gràcia, formerly strangers to each other, were mobilised in a restless effort to prevent the development plans and preserve the space as a neighbourhood facility. Their various protests were reflected in the Salvem el Jardí (Save the Garden) campaign in which they collected 7,000 signatures requesting that the plot passes to public property, urging the City Council to eventually buy it in 2014. Since then, the Associació Salvem el Jardí, have restored the remnants of the garden and thanks to their voluntary work, they have gradually transformed it into an open-air civic centre managed by the neighbours, a space they named Jardí del Silenci.
(Testimony from Marta Montcada, member of Associació Salvem el Jardí, Interview conducted in November 2023)
Today, the community garden is a hidden oasis in the neighbourhood, allowing visitors to enjoy the sounds, smells and tastes of nature. The garden is cared for by the volunteers-members of the association, and is open to the neighbourhood, hosting along with the tens of agricultural projects that contain multiple plant species, numerous social activities such as cultural and agricultural workshops, events, talks, exhibitions, shows, sport classes and playground equipment.
This is only one of the fascinating stories I learnt during my secondment in Barcelona, where I conducted on-the-ground research on the rich tapestry of community managed neighbourhood spaces. These are spaces of local character that operate as urban commons, meaning that they are run by the local communities, local organisations or any form of social institution established for their management, according to the local needs.
Over the course of three months, I was on my feet to get even a glimpse on the rich diversity that define these spaces in terms of program and typology, historical context, ignition, property status and management model. I conducted site visits engaging in informal discussions and formal interviews with numerous actors – members of the initiatives, with the urge to understand what these spaces are, how do they operate in the neighbourhood, what their relation to the City is, as well as what greatest challenges they face are. I visited community gardens and parks, neighbourhood cultural centres (Ateneus and Casals del Barri), working cooperatives, self-managed educational spaces, housing cooperatives and a self-sustainable agroecological community.
Below I summarise a few observations that derive from this experience, focusing on one of the dominant debates in the urban commons discourse, the relationship between the state and urban commons initiatives[1]. This relationship plays a key role in the character, resources and sustenance of the initiatives over time, especially when they operate on public property. Before exploring the array of relations, it is important to provide some overview of the emergence of these initiatives in Barcelona, as it is formative of the trajectories of these relationships.
Historical Context
The emergence of community-managed spaces in Barcelona is deeply rooted in the historic fabric of the city, encmpassing social movements and cooperativism. Examples of land collectivisations, initially by anarchist unions, were established before the Civil War. They evolved historically into workers’ collectives that self-organised to deliver services of healthcare, culture, education and production among others. During the 70s, the provision of these services and resources by communities themselves was a fundamental substitute to the state and market provision.
On the other hand, after the first democratic government in 1978, and particularly after the 2008 economic crisis, Barcelona has faced the challenges of a global city, such as the privatisation of public services, gentrification and massive tourism, evictions and an increase in precarious labour conditions, among others. Thus, the development of community managed services and spaces today is also a strong reaction to the current commodification of the city (Lain, 2015).
These two aspects of collectivism in Barcelona, both as a historic yield and a today’s countermovement, have shaped instances of different ideological values, priorities and self-reflected positions within the existing system of state and market.
Commons-state relationship
Conflict
Numerous examples illustrate a wholly conflicting relationship between the initiative and the City, primarily due to ideological matters. Such examples have often led to forced evictions, as seen in several cases of squats such as the social centre Can Vies in the neighbourhood of Sants, the original building of the social centre Banc Expropriat[2] which later reopened in a new location and the housing squat that pre-existed on the site of the Ca La Trava community gardens[3], both in the neighbourhood of Gràcia within two blocks’ distance.
Tolerance / indifference
In other cases, while the state is by any means supportive to the initiative, it demonstrates tolerance, at least until conflicting interests of development emerge and a conflicting relationship occurs such as in the examples discussed earlier. Similar to the previous cases, the “commoners”[4] are equiped with activist values, aware that they might need to defend their existence if such conflicting plans are in place. This is the case of the current initiative of Ca La Trava[5] and Jardi L’Alzina in Gràcia[6]. [7]
Collaboration
While the above cases demonstrate opposing relationship that is also strongly related to anarchist and anti-systemic collectives, Barcelona showcases several degrees of cooperation between the City and community managed spaces. Provision of space, funding and technical support by the municipality are among the most common collaborations supported by existing policies, such as the Patrimonio Ciudadano. A fundamental requirement is that the initiative demonstrates a local impact. This support is based on the ground of recognising the significant contribution of community-run initiatives in delivering democratised social services that respond to the specific and dynamic needs of each neighbourhood. The provision of spaces ranges from entire building complexes such as industrial sites, often of heritage value, run as cultural centres by federations of entities, such as the Can Batlló[8], and the Ateneu L’Harmonia[9]; to single buildings, managed as local points of reference for the neighbourhood life such as La Lleialtat Santsenca[10]; or parts of buildings co-hosted with other municipal facilities, such as Calabria 66[11]; and finally to open spaces, such as the case of Jardins d'Emma[12].
Autonomy
Beyond the mentioned cases, there is a great number of initiatives in which the property of space and other resources belongs to the managing entity, be it an association, collective or local organisation. These cases, such as working cooperatives have the capacity to operate independently of the state. Due to limited resources or legal constrains, the collective action of these initiatives often prioritises their members over the public impact, yet in most cases expanding to open activities.
Closing Reflections and Acknowledgements
My time in Barcelona’s shared neighborhood spaces exceeded any expectations I had before arrival. Beyond their physical importance, these spaces constitute a vital part of community life, woven by collective aspirations and creativity. They are testaments to the power of collaboration, sharing and transformative change.
Reflecting on my research visit, I carry with me not just data but stories, experiences, and a deeper understanding of the intricate dynamics that shape these vibrant spaces. More than a personal experience, it has been a collective journey with the invaluable input of several people, who enriched my research and personal growth.
To this, I would first like to thank my secondment supervisor prof. Nuria Marti for her restless support at every step of the way, from working hand in hand with me, to accompanying me on visits. Furthermore, I am heartfully grateful to the extensive list of members of the initiatives I had the chance to visit, who generously shared their space, time and stories. Finally, my stay in Barcelona wouldn’t have been the same without my fellow ESRs -Annette, Saskia and Zoe- who, whether in person or from afar, shared their knowledge, experience, and many enjoyable moments!
---------
Notes
[1] For more information see Huron, A. (2017). Theorising the urban commons: New thoughts, tensions and paths forward. Urban Studies, 54(4), 1062–1069.
[2] Banc Expropriat is a shared space in the neighbourhood that operates outside markets and hierarchies. It is a social centre that hosts free activities open to all, such as language classes, sport sessions, craft workshops, film screenings, play areas, computer access, as well as a free shop of donated clothes, among others. As a space very well received by the local community, its eviction in May 2016 triggered the escalation of protests in the neighbourhood. More information on the history of Banc Expropriat and its current relocation can be found at https://bancexpropiatgracia.wordpress.com/
[3] Members of the social movement that occupied/lived in the squat, re-occupied the site of the demolished building and created community gardens.
[4] People that manage the urban commons space.
[5] More information at https://www.instagram.com/ca_la_trava/?hl=en
[6] More information at https://www.salvemlalzina.org/
[7] This is also the case of Navarinou Park in Athens.
[8] More information at https://canbatllo.org/
[9] More information at https://ateneuharmonia.cat/
[10] More information at https://lleialtat.cat/
[11] More information at https://calabria66.net/
[12] More information at http://jardinsdemma.org/
---------
References
Lain, B. (2015). New Common Institutions in Barcelona : A Response to the Commodification of the City ? 2014(March), 19–20.
Author:
A.Pappa
(ESR13)