Pappa, A., & Paio, A. (2023, March). Local partnerships and urban governance: The case of Lisbon. In Diaconu, A. (Ed.) Proceedings of the RE-DWELL Grenoble Conference (pp. 58-61). Pacte Social Sciences Research Centre, University Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France.
https://www.re-dwell.eu/activities/conferences/grenoble
Posted on 08-12-2022
Collaborative forms of governance in urban regeneration are increasingly gaining ground in cities around the world, contributing to the active engagement of citizens in decision-making processes that affect their neighbourhoods and lives. In some cases, municipalities even attempt to embrace local grassroot initiatives led by active citizens, who creatively invent ways to regain and co-manage the urban commons. Extrapolated In the urban scale, such initiatives create networks of social practices of commoning that foster platforms of individual and collective rights (Stavrides, 2016) and help citizens reclaim the urban value (Borch & Kornberger, 2015).
In a similar vision, the Department of Housing and Local Development of the Municipality of Lisbon launched in 2011 a participatory budget program, namely BIP/ZIP, that serves as an instrument of public policy. The aim of BIP/ZIP is to annually fund bottom-up initiatives led by local partnerships in 67 priority neighbourhoods that enable responses to social and territorial emergencies. As of its 2021 edition, the program has funded 426 projects, involving 1403 different partner entities.
The aim of this research is to investigate the matrix of local partnerships that have been formulated throughout the eleven years of BIP/ZIP and understand their dynamic role for the city of Lisbon. The methodology employs data analysis and qualitative coding methods (Saldana, 2021) to (i) a map the complex networks of partners, and (ii) explore the transformation of the urban governance through the emerging roles of different types of partners – organisations.
References
Borch, C., & Kornberger, M. (2015). Urban commons: Rethinking the city. Routledge.
Saldana, J. (2021). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
Stavrides, S. (2016). Common Space: The City as Commons. Zed Books London.
Related vocabulary
Public-civic Partnership
Area: Community participation
Created on 08-11-2023
Read more ->Blogposts
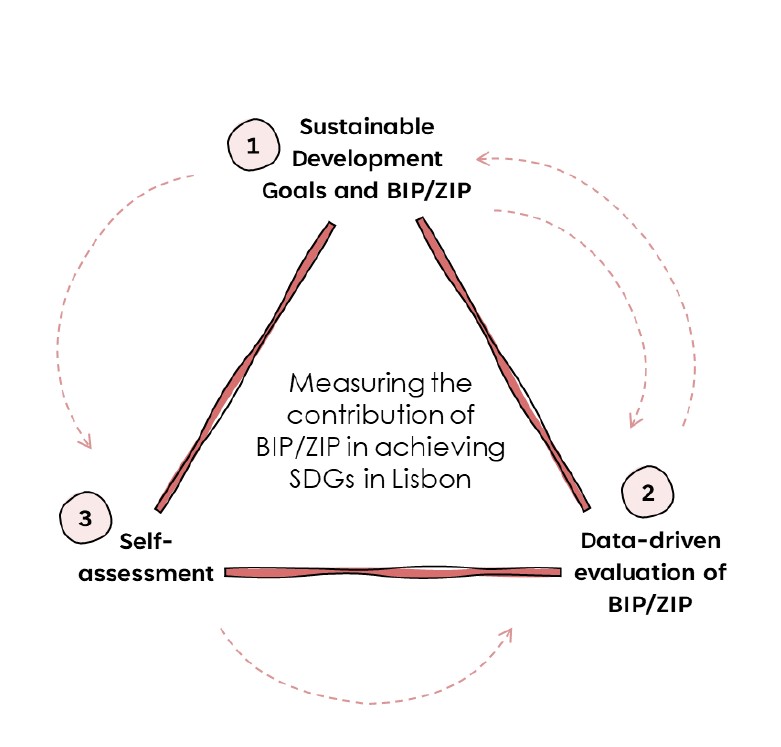
Participatory budgets and Sustainable Development Goals
Posted on 29-10-2022
Secondments
Read more ->